Stomach (Gastric) Cancer
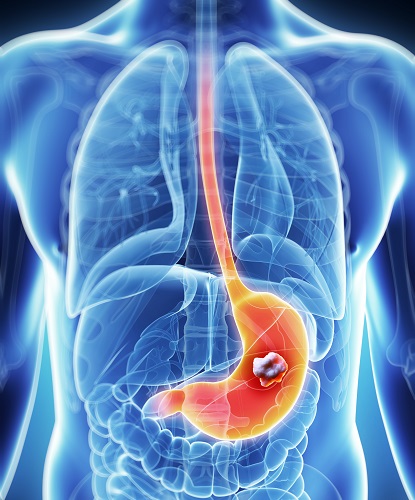
What is the stomach cancer?
The stomach lies in the upper part of the abdomen, just below the ribs. It has an important role in food digestion. The food that we eat passes down the oesophagus (gullet) and into the stomach. The stomach produces acid and enzymes to help digest the food. Once broken down, the food then passes into the small intestine for further digestion.
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, develops when the cells lining the stomach wall become abnormal and grow uncontrollably. The cancer can grow in any part of the stomach and if not removed, it can spread to surrounding lymph nodes or other organs of the body, namely the liver, lungs , bones and ovaries (in women).
What causes stomach cancer?
Doctors are not sure what causes stomach cancer and why certain people develop this disease. However, there are certain risk factors that increase the chance of developing stomach cancer.
These include:
- Ageing. Stomach cancer is more common in older people
- Gender. Stomach cancer is two times more common in men than women
- Diet. There is a strong correlation between diet high in smoked, pickled and salted foods and stomach cancer. Eating plenty of fruit and green vegetables can reduce the risk
- Smoking. Smokers have a higher chance of developing stomach cancer
- Pernicious anaemia, which causes a lack of vitamin B12, increase the risk of stomach cancer
- Chronic infection of stomach with a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori may lead to a slightly increase risk of stomach cancer
- Family history of stomach cancer
- Previous partial removal of stomach for whatever reason
What are the symptoms of stomach cancer?
When the cancer is small or in the early stage, there can be no signs or symptoms. However there are some alarming symptoms that require further evaluation.
These include:
- Upper abdominal pain or discomfort
- Indigestion
- Sense of fullness after eating even a small meal
- Weight loss or loss of appetite
- Persistent vomiting
- Passing of black, tarry stools
- Unexplained anaemia
- Feeling tired and lethargy
How is stomach cancer diagnosed?
Once you are suspected of having stomach cancer, your doctor will arrange for you to undergo a gastroscopy(endoscopy), where a thin, flexible telescope (gastroscope) is inserted into your stomach to look for any suspicious growth. If present, your doctor will take some tissues and send them to a pathologist who will examine them under a microscope. If cancer is confirmed, the next step is to stage the disease, usually with CT scan, to determine if it has spread. Staging also helps the doctor to decide which treatment option is best for you.
How is stomach cancer treated?
Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy ( and sometimes radiotherapy). The treatment recommednded by your doctor will depemd on the stage of the disease and general health.
Surgery
Surgery involves removal of the affected part of the stomach or occasionally the whole of the stomach. In the early stage of the disease, surgery can achieve a cure. Even in advanced stage where a cure is not achievable, surgery may still be required to improve the pateint’s symptoms for example to remove blockage caused by the cancer.
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy
Depending on the stage of the disease, one or a combination of the abovementioned treatment may be needed. Chemotherapy is the use of anti-cancer drugs to kill cancer cells and stopped them multiplying whereas as radiotherapy uses high energy radiation beam to achieve similar effects.
Sometimes chemotherapy or radiotherapy may also be required after surgery. This is also known as adjuvant therapy. The purpose is to kill cancer cells that may have escaped from the primary tumour.

